A Thorough Deep Dive into the Breadth of Gynecology Problems Involving the Ovaries, Uterus, Vagina and More
“Get an extensive knowledge of gynecology problems and disorder”.
Gynecology problems are basically health issues in the female reproductive organs which include the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and external genitalia. Some gynecology problems are common which women can face at some point of their life. But some gynecological disorders are serious and can affect a woman’s childbearing abilities and her sexual function. This blog will give you detailed information about gynecology problems.
Quick information in this blog
Different types of gynecology problems along with their symptoms and causes.
There are different types of gynecology problems some of them are:
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome(PCOS
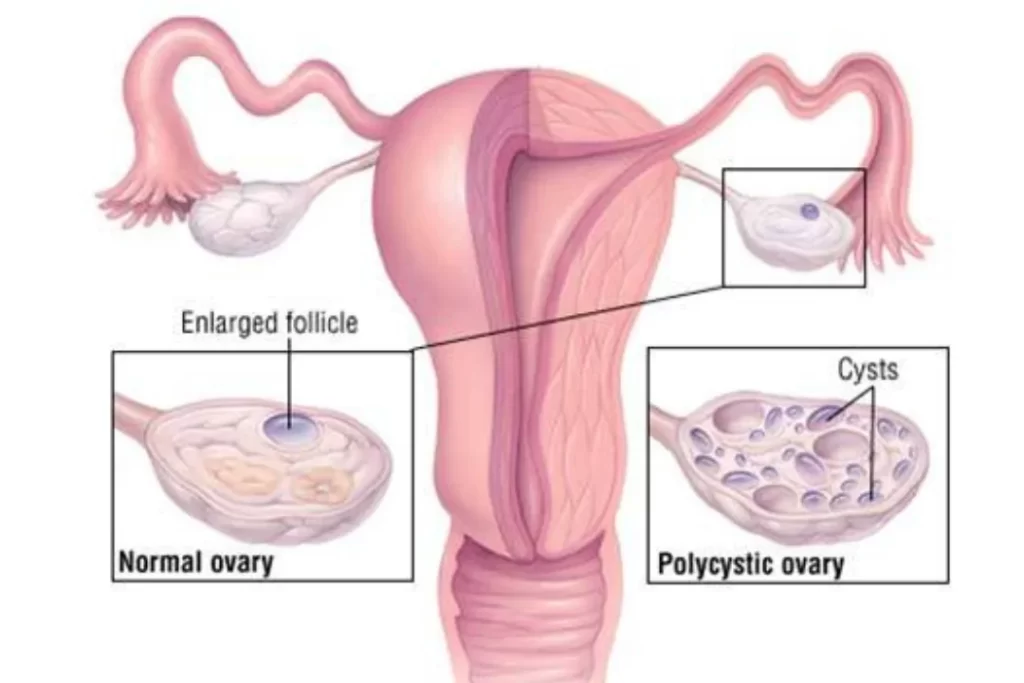
Polycystic ovary syndrome is one of the most common gynecology problems in women of reproductive age. PCOS is characterized by multiple small cysts in ovaries.
Symptoms
❖ Irregular periods, missed periods, or very light periods
❖ Infertility
❖ Ovaries that are large or have many cysts
❖ Weight gain
❖ Acne or oily skin
❖ Baldness or thin hair
Causes
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown but there are some significant factors which can cause it.
Excessive production of insulin
The excess level of insulin in the body might increase androgen production which causes difficulty with ovulation.
Low- grade inflammation
According to a recent study, females with PCOS have low-grade inflammation, causing increased levels of androgen production and this can lead to heart attack or blood vessels.
Heredity
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a genetic condition that sometimes runs in families. If any family member such as your mother, grandmother, aunt, or sister has PCOS then you have an increased risk of developing it. This suggests that sometimes genetic links can also cause PCOS.
Possible treatments
Polycystic ovary syndrome cannot be treated but its symptoms can be managed by following these steps.
❖ Weight loss
❖ Medication
❖ Regular exercise
❖ Reducing carbohydrate consumption
Uterine Fibroids
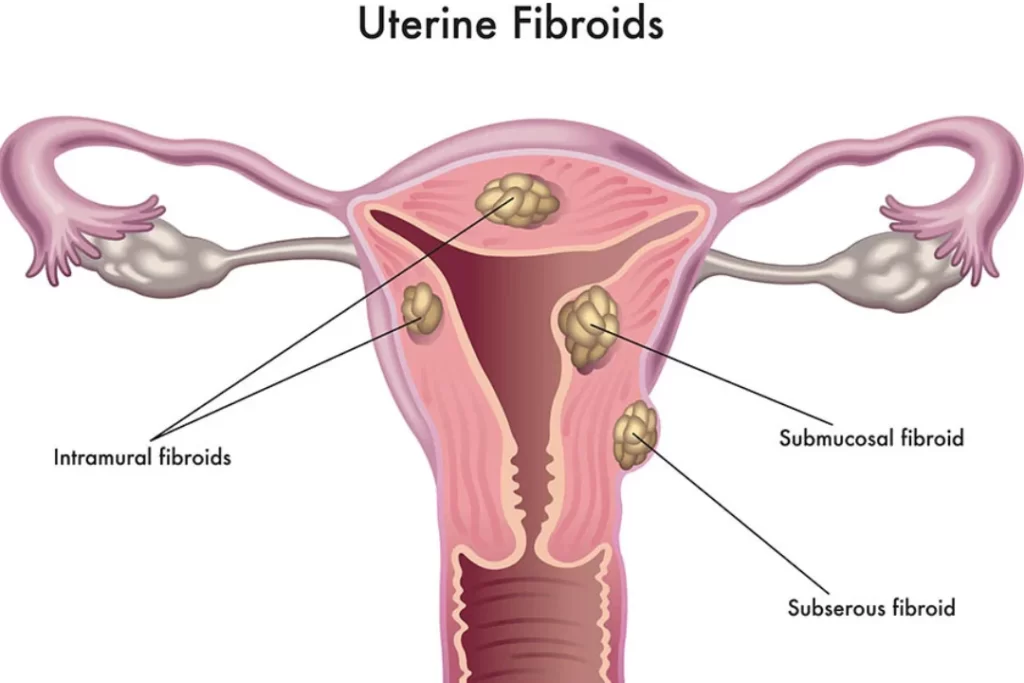
Uterine Fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. The growths are made of muscles or fibrous tissues and vary in size. All fibroids don’t have symptoms but when they have, they include:
Symptoms
❖ Heavy or prolonged periods
❖ Bleeding between periods
❖ Backache
❖ Pain or pressure in the pelvic area
❖ Frequent urination
❖ Constipation
❖ Pain during sex
❖ Enlarged abdomen
Causes
The causes of uterine fibroids are unclear but gynecologists believe that Estrogen and Progesterone hormones play a role in causing uterine fibroids . Mostly fibroids develop in the reproductive age. Moreover, according to the studies fibroids tend to grow when hormone level is high and shrink in decreased levels of hormones.
Types of uterine fibroid
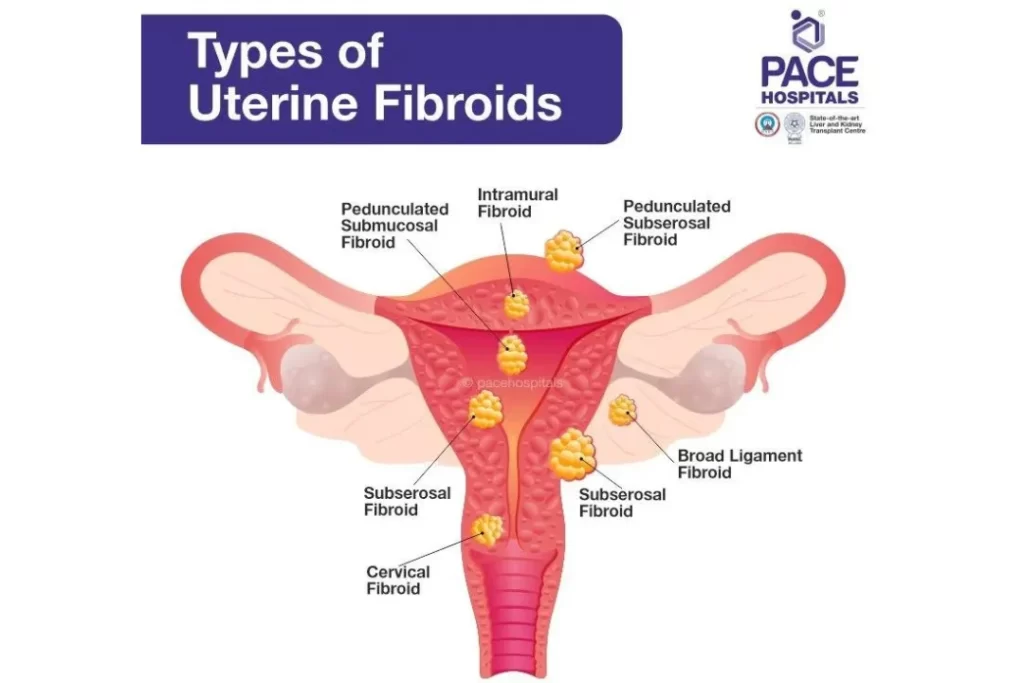
There are different types of uterine fibroids such as;
Intramural fibroid
These are the most common types of fibroid which are implanted into the muscular wall of the uterus.
Submucosal fibroids
These fibroids grow under the inner lining of the uterus.
Subserosal fibroids
This kind of fibroid grows under the lining of the outer surface of the uterus. Its size can enlarge and grow into the pelvis.
Pedunculated fibroids
These fibroids are attached to the uterus with a stem. They are also known as mushroom-like because of having a stalk and a wider top.
Tests and diagnosis
Although in many cases a gynecologist discovers uterine fibroids through a Pelvic Exam due to some symptoms it is preferred for diagnosis. There are different types of tests that can be done to confirm fibroids and determine their size and location. Some of them are:
Ultrasonography
This imaging test creates a picture of internal organs with sound waves.
Computed tomography (CT)scan
A CT scan uses X-ray images to make a detailed image of internal organs from different angles.
Magnetic resonance image(MRI)
MRI creates a detailed image of internal organs with the help of magnetic and radio waves.
Hysteroscopy
In hysteroscopy a device is used that is called a scope. It’s a thin, flexible tube with a camera on the end. The scope is passed through the vagina and cervix and then inserted into the uterus.
Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
This is a detailed X-ray where a contrast material is injected and then the X-rays of the uterus are taken.
Laparoscopy
In laparoscopy, a patient gets a small incision in the lower abdomen. Then a thin and flexible tube, having a camera on its end, is inserted to get more visibility of the organs.
Menstrual Disorders

Menstrual problems cause disturbance in a woman’s normal menstrual cycle. It is one of the most common reasons why women visit gynecologists. Menstrual problems and their symptoms really affect a woman’s life. It can also cause problems in conceiving.
Symptoms
- Abnormal menstrual bleeding
- Pain and cramping
- Depression
- Headaches
- Bloating or fullness in the abdomen
- Emotional stress
Causes
- Hormonal imbalance
- Cancer
- Uterine fibroids
- Clotting disorders
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Genetics
Types of Menstrual Disorders
If a woman experiences one or more of the symptoms before or during the period causing problems, she may have a menstrual cycle “disorder.” These include:
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)
AUB is a prolonged and extremely heavy bleeding that can be caused by fibroids, polycystic, hormonal change, and cancer in rare cases.
Dysmenorrhea
In simple word, dysmenorrhea is a painful period. More than half of the women have some pain for one or two days and usually, this pain is mild. But some women have really severe pain which causes disturbance in their daily routine.
Amenorrhea
Amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation and is defined as missing one or more menstrual periods. Physiological states of amenorrhea are most commonly seen during pregnancy and lactation. Moreover, there are two types of amenorrhea Primary Amenorrhea and Secondary Amenorrhea.
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
Premenstrual syndrome is the combination of symptoms that many women have before one or two weeks of their periods. Study shows that 90% of women have premenstrual symptoms which may include; bloating, headaches, and mood swings.
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
The premenstrual dysphoric disorder is a gynecology problem that is alike premenstrual syndrome but it is more serious. PMDD causes severe irritability, depression, and anxiety before menstruation and these symptoms end after two or three days after periods start. Women having a history of major depression, postpartum depression, or mood disorders are at higher risk for PMDD than other women.
Ovarian cancer
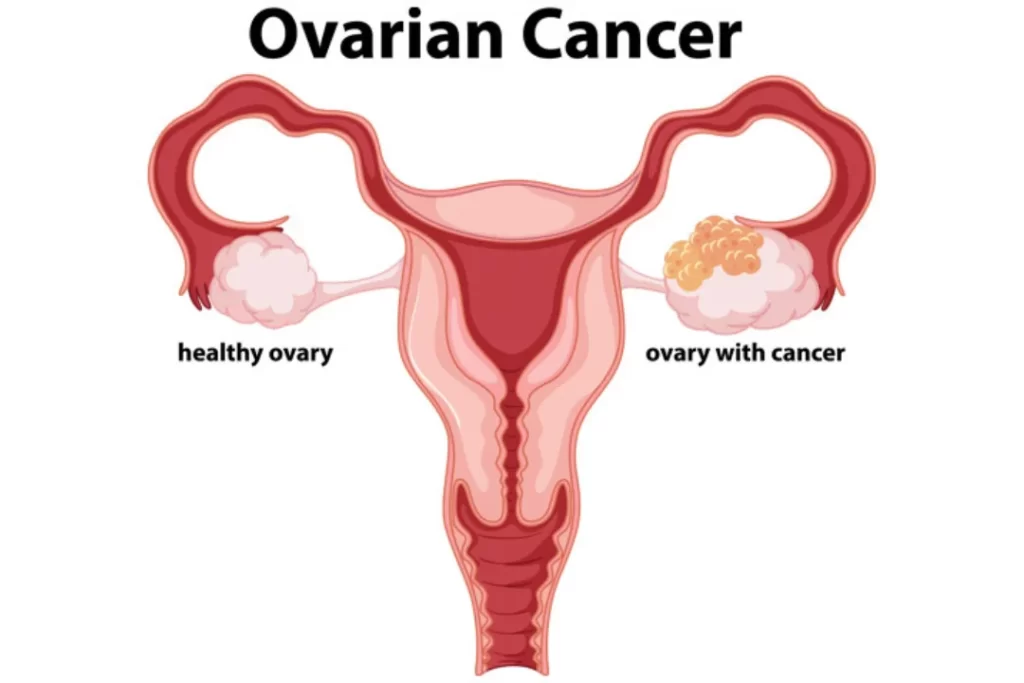
Ovarian cancer is an abnormal growth of cells in the ovaries. The female reproductive system is comprised of two ovaries of almond size on each side of the uterus. As a result of irregular and uncontrolled growth of cells, it invades and damages other normal tissues.
Symptoms
- Pain or pressure in the pelvic area
- Abdominal bloating and swelling
- Fatigue
- Frequent urination
- Changes in bowel habits
- Weight loss
Causes
There are different factors that can cause ovarian cancer but mostly it is a result of mutation in DNA. Due to cell division, it becomes uncontrolled and it results in the formation of clumps of abnormal cells which is termed a tumor.
Types of ovarian cancer
The type of ovarian cancer varies according to the types of cells where the cancer begins These types can be classified as:
Epithelial ovarian cancer
This is the most common type of ovarian cancer which has several subtypes such as serous carcinoma and mucinous.
Stromal tumors
These tumors usually have been diagnosed at an early age rather than other ovarian cancers.
Germ cell tumors
This type of ovarian cancer mostly develops at a younger age.
Risk factors
- These are the factors that can increase the risk of having ovarian cancer.
- Older age
- Inherited gene changes
- Family history of ovarian cancer
- Obesity
- Having no pregnancy
Endometriosis
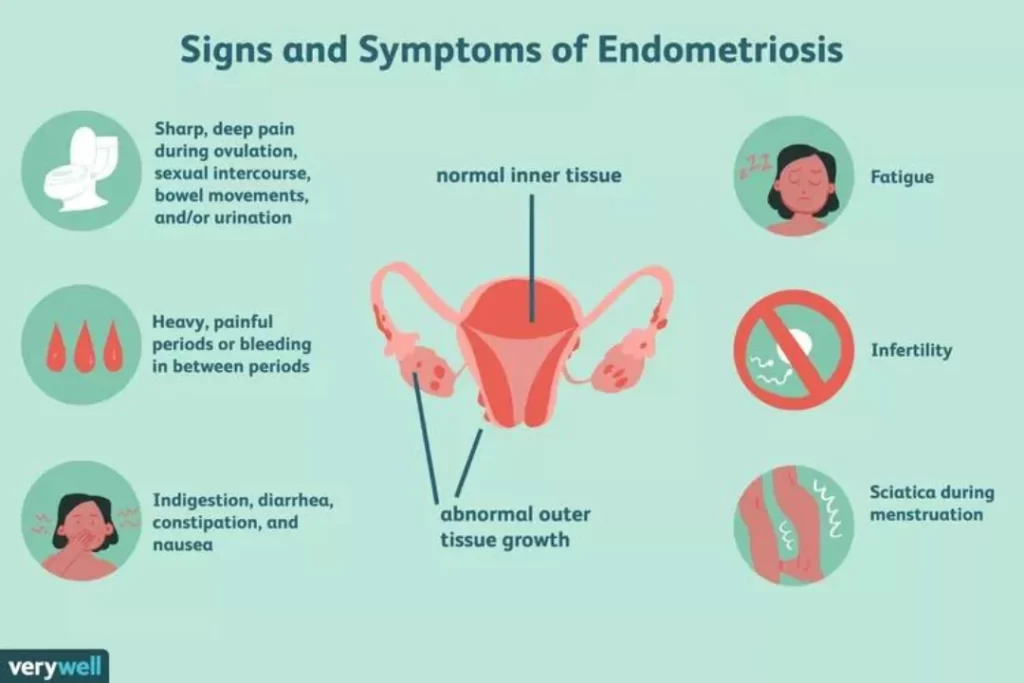
Endometriosis is a condition in which the inner tissues of the uterus grow outside the uterus .it’s a painful condition that affects ovaries and fallopian tubes as well. Endometriosis lining slows off during the menstrual cycle. When endometriosis affects ovaries a cyst is formed that is called endometriosis. It enters other surrounding cells and causes irritation. Endometriosis causes severe pain in the menstrual cycle and sometimes infertility results but medications can decrease the severity of disease and other related complications.
Symptoms
- Painful bowel movement
- Pain during menstrual cycle
- Pain during intercourse
- Excessive blood flow
- Infertility
Some other symptoms can be fatigue, diarrhea, constipation, bloating and nausea.
Causes
Some possible causes can be :
- Transformation of peritoneal cells
- Retrograde menstruation
- Complications of surgical scar
- Changes in embryonic cell
- Transport of endometrial cell
- Condition of the immune system
Cervical dysplasia
In this gynecology problem, abnormal cells grow on the surface of the cervix which is the lower part of the uterus . Abnormal changes in cells can be mild, moderate, and severe as well. It is detected by a pap test and diagnosed with a biopsy. Having cervical dysplasia doesn’t mean you have cervical cancer but it can lead to cancer if remain untreated.
Symptoms
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Bleeding during menopause
Causes
Cervical dysplasia is mostly caused by Human Papillomavirus (HPV), the most commonly sexually transmitted disorder in the United States. There are more than 200 types of HPV but a few can be cancerous.
Diagnosis and Tests
- Colposcopy
- Biopsy
Incompetent cervix
An incompetent cervix means the cervix is too weak to accomplish normal pregnancy it mostly results in the premature birth of a baby In normal pregnancies cervical opening becomes close and opens at the time of child birth but in the case of an incompetent cervix, it opens too early to complete normal gestation period. It is also responsible for miscarriages.
Conclusion </b?
To sum up, hopefully, this elaborative and detailed discussion will give you a deep knowledge of gynecology problems in women’s lives. Every woman should have awareness about these gynecology problems, their symptoms, their complications, and their preventive measure as well. Because after having a better knowledge of these problems you can get that timely medication can lessen the severity of the disease.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS </b?
What are the preventive measures for gynecological problems?
Having a balanced diet, maintaining good hygiene, practicing safe sex, managing stress levels, and having regular gynecological check-ups can help you to prevent some gynecology problems.
What is the difference between gynecology and obstetrics?
Obstetrics includes care during pre-conception, pregnancy, childbirth, and immediately after delivery while gynecology involves care of all women’s health issues.
Are gynecology problems related to a specific age?
No, gynecology problems can affect women of all ages, from adolescence to menopause.